Who doesn’t want a clear and flawless skin? Almost everyone does! Acne is not only unsightly but is a cause of both physical and mental discomfort to the bearer as well. It may present itself in various forms such as seborrhea, comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, cysts and eventually scarring of skin. In this blog I will be talking about what is acne and what causes it.
There are three problems with acne.
- First, it is an obstinate skin condition that heals very slowly and does not go away readily.
- Second, even if they go, some forms of pimples are disfiguring and leave an undesirable scar behind and
- Third, their recurrence.
Before I share my experience on the treatment of acne, let us first understand what acne is and how and why do you get them on your face.
What is Acne?
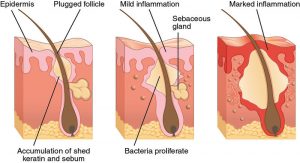
How Acne is formed
Acne is a skin disorder characterized by tiny red bumps or pimples on the skin surface caused by infected and inflamed oil glands. Another term for it is acne vulgaris. It is mainly prevalent among teenagers though may present at any age. It occurs in people with overactive oil glands (sebaceous glands) that secrete excess oil (sebum) blocking the tiny openings for hair follicles. These pores get clogged (clogged pores) with oil and debris from dead skin cells. With time, bacteria start proliferating in these pores leading to infection and inflammation and the pimples appear red, hot swollen and painful.
Why do you get acne on your face?
The process of acne formation can be defined in four steps2:
- Increased sebum (oil) production from oil glands
- Multiplication (proliferation) of cells inside the follicles
- Colonization of bacteria (commonly P.acnes and Staphylococcus aureus) inside the follicle
- Inflammatory reaction
Process of Acne formation
Normally, the oil glands present deep within our skin pores are connected to the skin surface through a duct called follicle. This set up is called Pilosebaceous Unit (PSU). Under hormonal influence (Androgens) Squamous epithelial cells (the cells lining the PSU), sebaceous cells (that produce sebum or oil) and keratinocytes (that produce hair cells) gets activated and start proliferating. As the cell proliferation of all the three types of cells increase, they form a plug. Pressure builds up inside the PSU, due to which oxygen supply is cut off for cells deep down the unit, limiting their metabolism1. This anaerobic environment along with excessive oil (sebum) provides a congenial and nutritive environment for bacterial flora (most commonly Propionibacterium acnes) to colonize and flourish within the PSU. When the pressure inside the plugged PSU reaches to the point that is unbearable, it bursts and the contents are exposed.
Body’s defense mechanism (neutrophil cascade) comes into action and inflammation begins at the site resulting in the formation of inflammatory varieties of acne such as papule, pustule, nodule and cysts. Pimples commonly appear on the face and forehead but can also be seen on upper back, shoulders and chest area.
What are the types of Acne?
Acne includes a variety of spots on the skin such as blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, nodules and cyst.
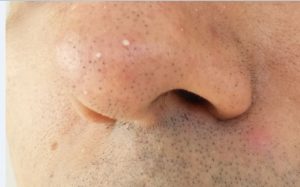
Blackheads & Whiteheads
What are Blackheads and Whiteheads?
Blackheads are also called open comedones because of incomplete blockage of follicular openings. They are less elevated dark bumps on the skin. Whiteheads (closed comedones) results from complete follicular blockage. They are white in color and firmer in consistency. Both of these comedones are mild forms of pimples, involve no inflammation and can be managed with home remedies. This is usually found on the nose, chin and forehead.
What are Papules, Pustules?
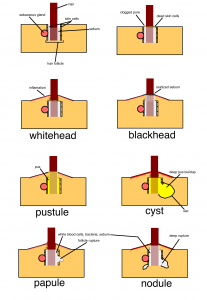
Types of Acne
Papules are small red bumps that are painful to touch. Pustules are filled with pus and have a white tip in the centre. They develop when clogged skin pores become inflamed and infected with bacteria. Papules and pustules are superficial inflammatory lesions and are of moderate severity that can be managed with home remedies. If they persist, you may want to seek medical attention.
What are Nodules and Cyst?
Nodules are formed beneath the skin surface and are larger, painful and harder in consistency. Cysts are large and painful pus filled lumps and the most severe of all types of zits. They most often leave scars behind. Both nodules and cyst need proper medical attention.
Causes of Acne
While all of us harbour P. acnes (Acne causing bacteria), only few develop pimple problem. Why is it that some of us suffer with this problem gravely, while others may have few pimples sporadically in their entire life? Why only few people acquire acne problem? The answer to this question lies in a variety of aggravating and precipitating factors. Although acne is predominant in puberty, lots of adults also develop this problem. Adult acne is explained as the one seen beyond 25 years of age. In puberty, males are affected more commonly whereas adult acne mainly affects females.
-
-
- Hormones: Most probable cause of pimples is the changes in hormone activity namely androgens during puberty. Under the influence of hormones, the oil glands start producing excessive oil that leads to clogged skin pores, subsequent bacterial proliferation and pimple formation.
- Foods that worsen or ameliorate symptoms of acne: No single food can cause pimples or treat its symptoms but definitely can worsen or reduce the severity. Foods rich in vitamin A and D can have important effect in reducing acne. And foods with high glycemic index (foods that causes your blood sugar shoot up quickly such as refined sugars and white bread), dairy products, can worsen it.3
- Family history: Pimples can be transmitted in genes from parents.
- Stress: There is a vice versa relationship between pimples and stress which means when stress levels increase there is more acne formation. Similarly, pimples have a profound psychological impact especially on the teenagers as it affects their self esteem. So, acne can lead to stress. Stress positively correlates with acne severity 4.
- Underlying medical condition: Sometimes acne indicates some serious underlying medical condition in women such as polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD) requiring medical attention.
- Other factors that influence pimple formation are occupation, menstruation, ultra violet radiation, seasonal variation (summer month shows exacerbation) and excessive sweating.
-

Acne is one of the most commonly occurring skin diseases which can be classified as either non-inflammatory (blackheads and whiteheads) or inflammatory (papules, pustules, nodules and cysts). Milder variants of this disease can be easily managed with home remedies. However, medical intervention is needed for moderate to severe types of pimples. Although it is seen in all walks of life in almost all people but it appears predominantly in the puberty with prevalence in this age group being 95%.5 As more and more microorganism are developing resistance to common antibiotics, there is need to shift to natural methods of cure. To read about home remedies to remove pimples, please Click Here.
References
-
- Lynn DD, Umari T, Dunnick CA, Dellavalle RP. The epidemiology of acne vulgaris in late adolescence. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2016;7:13-25. Published 2016 Jan 19. doi:10.2147/AHMT.S55832
- Rathi S.K. Acne vulgaris treatment : the current scenario. Indian J Dermatol. 2011;56(1):7-13.
- Spencer EH, Ferdowsian HR, Barnard ND. Diet and acne: a review of the evidence. Int J Dermatol. 2009 Apr;48(4):339-47.
- Zari S, Alrahmani D. The association between stress and acne among female medical students in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:503-506. Published 2017 Dec 5. doi:10.2147/CCID.S148499
- Skroza N, Tolino E, Mambrin A, et al. Adult Acne Versus Adolescent Acne: A Retrospective Study of 1,167 Patients. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11(1):21-25.





Utterly composed written content, thankyou for information .
Thanks. I am glad you liked it. To read my article on how to remove pimples, please refer to the link below.
https://www.keytoperfecthealth.com/how-to-remove-pimples/
Happy reading!
Thanks for sharing, really useful :)!
Thankyou Johnny..Nice to know you found the post useful:)
Enjoyed the post.
Thankyou!
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Rarely do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and entertaining, and let me tell
you, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something that too few men and women are speaking intelligently about.
Now i’m very happy I came across this in my hunt for something relating to this.
Thankyou for your valuable comment!
Very descriptive post, I enjoyed that bit. Will there be a part 2?